Botox Affects the Functioning of Which of the Following Neurotransmitters
Botulism the toxin in botox effects muscles by preventing the release of the neurotransmitter actylcholine. The pharmacological action of Botox is due to the light chain which causes protease activity within the neuron which leads to inhibition of neurotransmitter exocytosis.

Neurotransmitters Types Function And Examples Simply Psychology
Calcium is the ion that enters the cell to trigger the release of this neurotransmitter.
. It releases neurotransmitters that can cause the wrinkling of muscles. More 1 person found this helpful. Molecular Mechanisms of Botox Both the heavy chain and the light chain consist of two distinct domains.
Botulinum toxin BoNT often shortened to Botox is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species. Botulinum toxin induces weakness of striated muscles by inhibiting transmission of alpha motor neurones at the neuromuscular junction. Substance P endorphins cholecystokinin CCK.
Transmission is also inhibited at gamma neurones in muscle spindles which may alter reflex overactivity. Botox calms the affected muscles and allows for a more natural and neutral positioning. Changing the shape of the synapse.
Note that the grey line is the normal AP graph while the black line is the graph for the toxin. These substances target the nervous system disrupting the nerve signaling processes that stimulate muscle contraction. Selected Botox - induced paralysis of facial muscles only affects facial expressions.
The purpose of these PET scans was to map areas of the brain that perform certain functions. Acetyl coenzyme A usually found in dietary fats and choline a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells. Synaptic vesicles store and carry neurotransmitters within the axon terminal.
What do the different colors on the scan tell researchers about how the brain works. Choline from dietary fats and acetyl coenzyme A both of which are acted on by choline acetyltransferase. What does Botox do.
For a long time we have known that the brain is plastic meaning that. Mimicking the effects of neurotransmitters c. The toxin causes the disease botulism.
Now this acetylc View the full answer. Question 2 0 out of 25 points People who find meaning in their lives in general and even in negative and tragic experiences are likely to _____. Botox is a neurotoxin.
Endorphins block the transmission of substance P a neurotransmitter that sends information about pain to the CNS. It is now well documented that the analgesic effects of BoNTA1 are related not only to its paralytic effect but also to an effect on the nociceptor system Wheeler and Smith 2013. BoNT-A can take up to two weeks to take full effect and its effects typically persist for four to six months until the neuron regenerates function Dolly Aoki 2006.
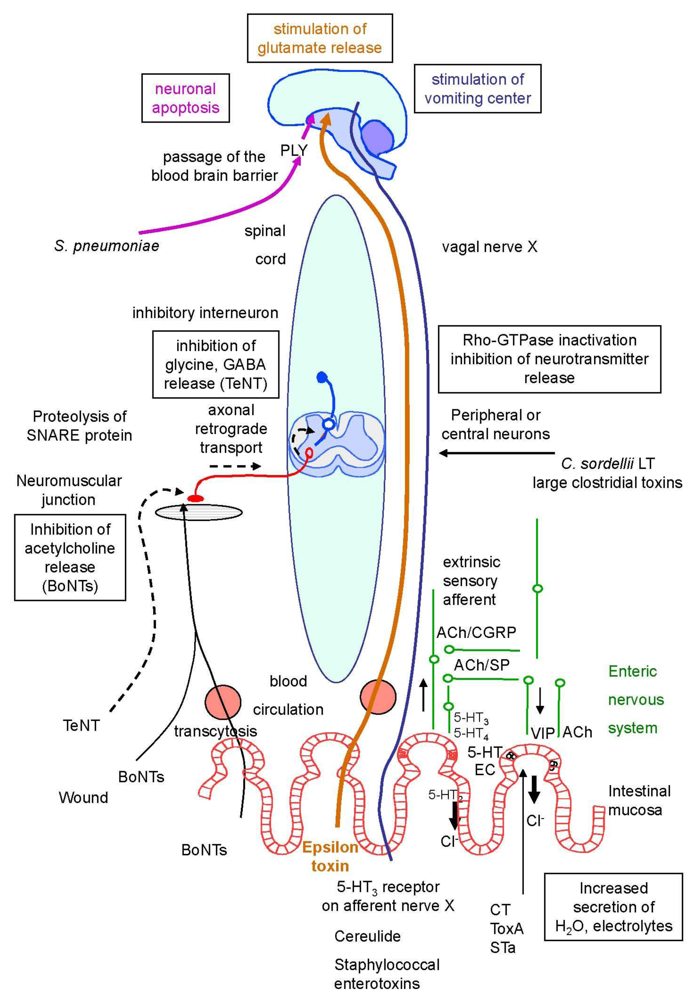
The toxin paralyzes muscles by blocking the release of acetylcholine the principal neurotransmitter between nerve and muscle. The release of this neurotransmitter is controlled by the membrane-associated proteins SNARE complex because in the presence of. At the muscle synapse however no neurotransmitter is released the muscle lies inert and thus no feedback about muscle movement is sent back to the brain from the periphery.
This is how the drug causes temporary muscle paralysis. If 100 excitatory neurons released their neurotransmitter from synapses on the. One of the primary functions of the reticular activating system is.
This figure presents views of activity in a persons cerebral cortex as imaged by positron emission tomography PET. This calcium diffuses into the cell and causes synaptic vesicles to release acetylcholine a neurotransmitter molecule. Botulinum toxin is injected by hypodermic EMG needle directly into the muscles blocking the connection between nerves and muscles.
The neurotransmitter that is normally released from motor neurons and responsible for triggering muscle contractions is acetylcholine. The cosmetic known as Botox affects the functioning of which of the following neurotransmitters. Which of the following graphs would best represent what the action potential graph would look like in a neuron treated with botulism.
This has led to its use in conditions with muscular overactivity such as dystonia. The widely reported antinociceptive effect of BoNTA1 would be primarily mediated by the blockade of neuropeptides and inflammatory mediators release and by the inhibition of plasma membrane. The addition of the effects of release of neurotransmitter from multiple synapses at the same time on the same neuron is __________.
Which of the following neurotransmitters is mimicked by the active chemical in marijuana. So the long and short there is no medical evidence that cosmetic Botox has any affect on the memory. As soon as action potential arrives at the presynaptic terminal it causes voltage-gated calcium channels to open.
It prevents the release of neurotransmitters that contract muscles. Name a few neuropeptides. It prevents the release of neurotransmitters that smooth out muscles.
In this case its causing the neurotransmitters that make the muscles move inhibited not the neurotransmitters in the brain which would have to do with memory and memory functions. The toxin is also used commercially. A carboxyl terminal and an amino terminal respectively Figure 1.
Dopamine epinephrine and norepinephrine. The cosmetic known as Botox affects the functioning of which of the following neurotransmitters. The injection of BOTOX into peripheral muscles has been shown to have therapeutic effects in a growing number of indications including disorders involving skeletal muscle eg strabismus blepharospasm cervical dystonia spasticity cosmetic smooth muscle eg bladder glands axillary hyperhidrosis and nociceptive pain eg.
It releases neurotransmitters that can cause muscle spasms. The amino acid tyrosine synthesized from the phenylalanine found in foods. Botulinum toxin works by blocking a neurotransmitter acetylcholine involved in muscle contraction.
Neuropeptides are larger compounds released alongside neurotransmitters that modulate communication between nerve cells. SOPHIA Human Biology Unit 3 Milestone 1 What is the effect of the drug Botox on neurotransmitters. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction thus causing flaccid paralysis.

Neurotransmitters Flashcards Quizlet

Pdf Botulinum Toxin And Its Clinical Aspects An Overview

Toxins Free Full Text Bacterial Toxins And The Nervous System Neurotoxins And Multipotential Toxins Interacting With Neuronal Cells Html
No comments for "Botox Affects the Functioning of Which of the Following Neurotransmitters"
Post a Comment